Types of Back Pain
Back pain is either chronic or acute. Both types of pain can disrupt your daily life, but acute pain typically lasts fewer than 6 weeks. For example, if you strain a muscle when picking up a box of books, you might have acute back pain. Chronic pain, however, lasts longer than 6 weeks and can actually become a disability. It’s more difficult to treat and often has deeper, more complex causes.
Common Causes of Chronic Back Pain
Chronic back pain may stem from several causes. Spinal stenosis (when the spinal canal narrows and causes nerve pain), problems with discs (such as herniated and bulging discs), arthritis of the spine, spinal cord injuries, and myofascial pain syndrome can all cause chronic back pain. After conducting a thorough physical examination, which may include imaging, the pain specialists at Mays & Schnapp can determine the underlying condition causing the problem and propose a treatment plan to help keep the pain under control.
When to Seek Help From a Back Pain Doctor
Seek help from a pain management specialist when your pain continues for an extended period of time, is severe, or doesn’t respond well to common treatments like over-the-counter pain medicine such as NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), which include naproxen, ibuprofen and aspirin.
You might also want to visit a specialist if your pain is accompanied by tingling or numbness in your limbs. If you want to try alternative treatments that regular doctors don’t provide, a back pain doctor may be the right choice for you.
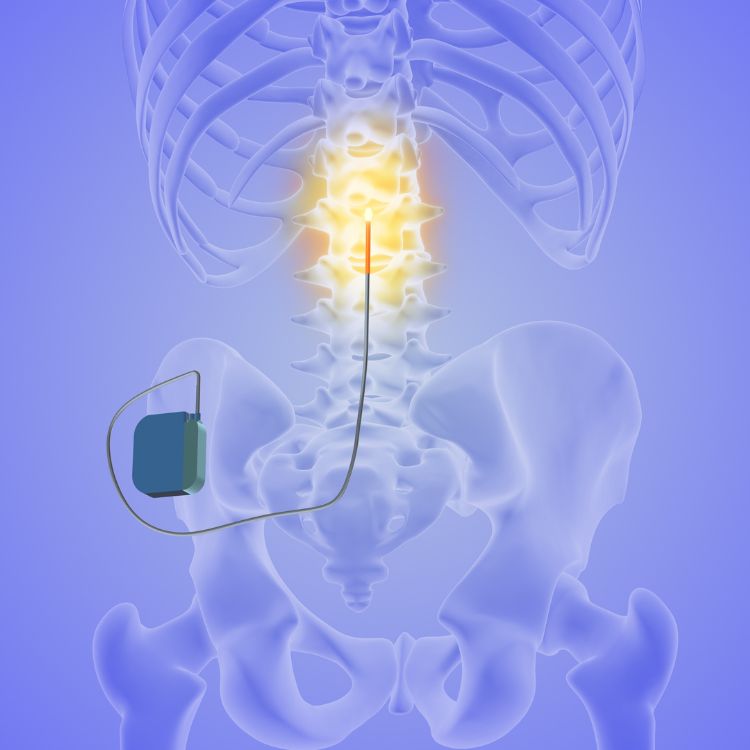
Treatment for Back Pain
Your back pain doctor might suggest a number of treatments for your chronic pain. Physical therapy is one option, and a physical therapist can suggest exercises you can try. Massages may work well for you, too. Injection-based procedures are becoming more popular, and one study after another has provided evidence that injections can help with chronic back pain. Injections include nerve blocks, nerve ablations, and epidural steroid treatments.
A pain management doctor may also suggest some use of pain medicine, such as muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory medications, to help provide relief as we address the underlying issue causing the pain. Treatment depends on your situation and medical history.